Full-Service Solution Design Solutions are the Ultimate in Business Transformation Expertise.
Designing For Results: An In-Depth look at the Definition of Solution Design
Solution designs are detailed plans created to address a specific business or technical problem. The solution can be a software, technology, process improvement, people solution or a combination of different types of them. Diligence in designing solutions is crucial to minimize errors and rework, ensuring that the final product meets the requirements effectively. A solution architect (solution designer) is responsible for whole process of solution design and deliver a set of solution design documents and additional information that provides a blueprint for stakeholders in solution design project lifecycle.

Importance of Solution Design
Solution design is a critical aspect of project development that plays a vital role in ensuring the successful implementation of complex IT systems. It involves creating a detailed blueprint or plan for the implementation of a specific solution to a problem or challenge. By investing time and resources in solution design, businesses can avoid costly rework, reduce project risk, and ensure that their software systems meet their business goals.
Why Solution Design Matters
Solution design matters because it helps businesses address specific business challenges and achieve their goals. It involves analyzing the requirements and constraints of the problem at hand and designing an effective solution that addresses those needs. A well-crafted solution design takes into account various factors such as business objectives, user requirements, technological constraints, and available resources. By prioritizing solution design, businesses can ensure that their software systems are scalable, efficient, and meet the needs of their users.
Building the Future: The Output of a Comprehensive Solution Design Process
A solution designer provides a detailed set of design documents. This typically includes information such as the solution’s architecture, components, interfaces, and interactions. Additionally, it also includes any necessary diagrams, flowcharts, or data models for any type of stakeholders in the organization. The software development lifecycle ensures that the designed software aligns with user expectations and technical constraints.
A good solution design is essential for ensuring that the designed solution meets the business requirements, goals and objectives, and that it can provide the value in optimal cost and other project scope elements. The output of solution architects tasks also serves as a reference for all stakeholders involved in the project, including the project manager, technical team, code writer, support service.
What is Included in Solution Design?
In software development methodology a solution architect produces a set of deliverables such as:
- A detailed project plan that determine the tasks, milestones, and timelines for the project managers.
- A list of hardware and software requirements for the end product.
- Outline how to test the end product, software or system during development and deployment phases with a detailed testing plan.
- Outline how to maintain and support the developed solution after it’s deployed with a maintenance plan.
- Educate users on how to use the solution with a set of user guidelines, training materials, and other documentation.
The output of the solution design is crucial to the success of the project as it lays the foundation for the implementation, testing, and maintenance of the solution. This ensures that the solution is aligned with the business requirements and goals and can be implemented and maintained effectively.
Lighthouse, as a managed service provider, plays a different role in solution design. We do not develop software systems or any end product. However, we determine the system components based on company needs. This includes both functional and non-functional requirements. We assist our customer by delivering a good solution design and assess vendors to find the best option.
Optimize Your Business With Tailored System Design for Every Industry and Challenge

Apply our methodology to any solution type. Here are a few examples of how we apply solution design in different types of businesses:
E-commerce
Solution design services to meet the business needs in the development of online stores and e-commerce platforms.. This includes designing the user interface, integrating with payment, and shipping components, and ensuring the platform is secure and scalable.
Manufacturing
Improve efficiency and productivity in a manufacturing company by using solution design. This may include designing automated software for tracking inventory and production or implementing advanced analytics to optimize production schedules.
Healthcare
Solution design services create healthcare-specific software to improve patient care and streamline administrative processes. This may include designing electronic health records systems, telemedicine platforms, and patient engagement management.
Financial Services
Use solution design to create financial software that meets the specific needs of the business. This may include designing accounting software, online banking platforms, and fraud detection systems.
Supply Chain
Use solution design to optimize the supply chain process, from sourcing raw materials to delivering products to customers. This may include designing logistics systems, supply chain management software, and inventory management systems.
Retail
Improve customer experience and optimize operations in a retail company by using solution design. This may include designing point-of-sale systems, inventory management systems, and customer relationship management systems.
A Behind-the-Scenes Look at the Work of Our Solution Designers
Expertise and Results: Unlocking Your Business Potential With OurSolution Design Services and Team
Our team of experienced solution designers and architects can help businesses unlock their potential by providing expert solution design services. We have a proven track record of delivering successful software solutions that meet the needs of our clients. Our solution design process involves working closely with stakeholders to understand their requirements, designing effective solutions, and implementing those solutions in a timely and efficient manner. By partnering with us, businesses can ensure that their software systems are designed to meet their business goals and achieve success.
What is Solution Design in a Project?
Our solution designers work closely with your organization to understand your company’s unique needs and goals. We design and implement a tailored solution that meets your specific requirements and creates value. Whether you need to improve efficiency, reduce costs, or increase revenue, our team has the skills and expertise to help you achieve your goals.
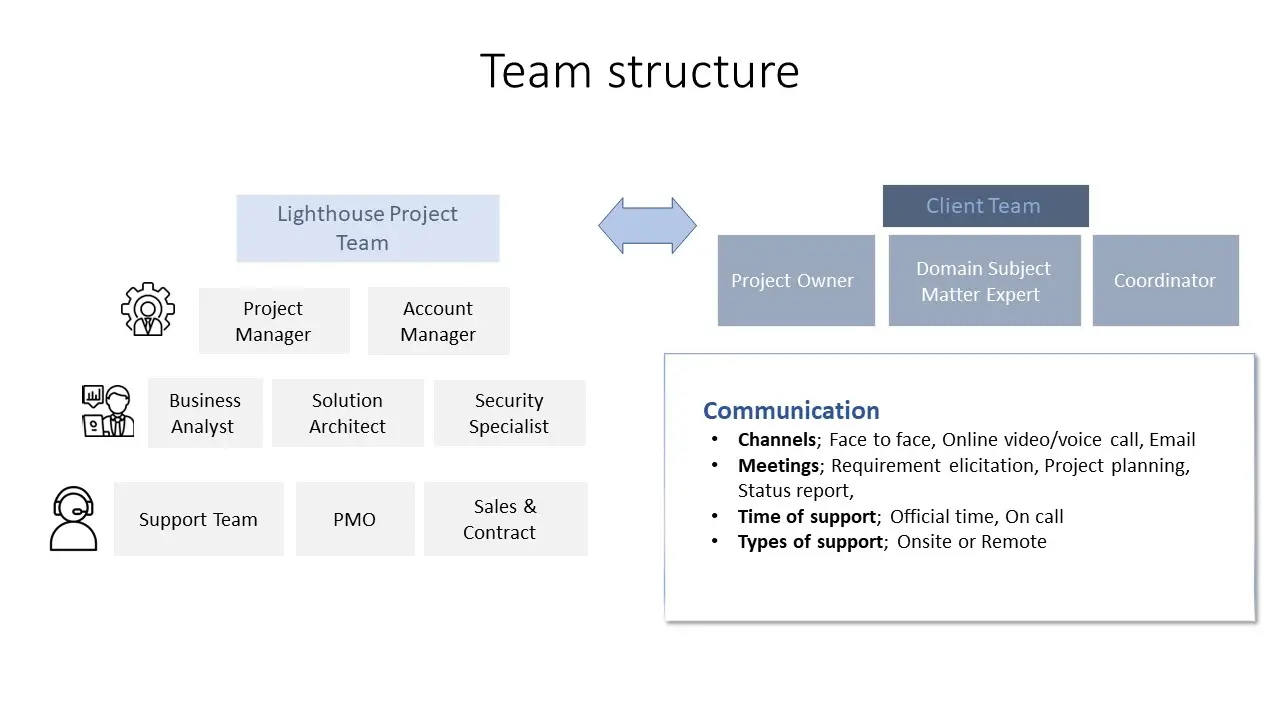
Our team dedicates to provide ongoing support and maintenance to ensure that your solution remains aligned with your business objectives over time. With our help, you can be assured that your solution will be designed and implemented with the highest level of quality and at optimal cost, meeting your business needs for years to come.
Implementing Software Solutions With Confidence: A Proven and Structured Solution Design Methodology
Lighthouse Solution Design PHASE and documentation includes the following steps:
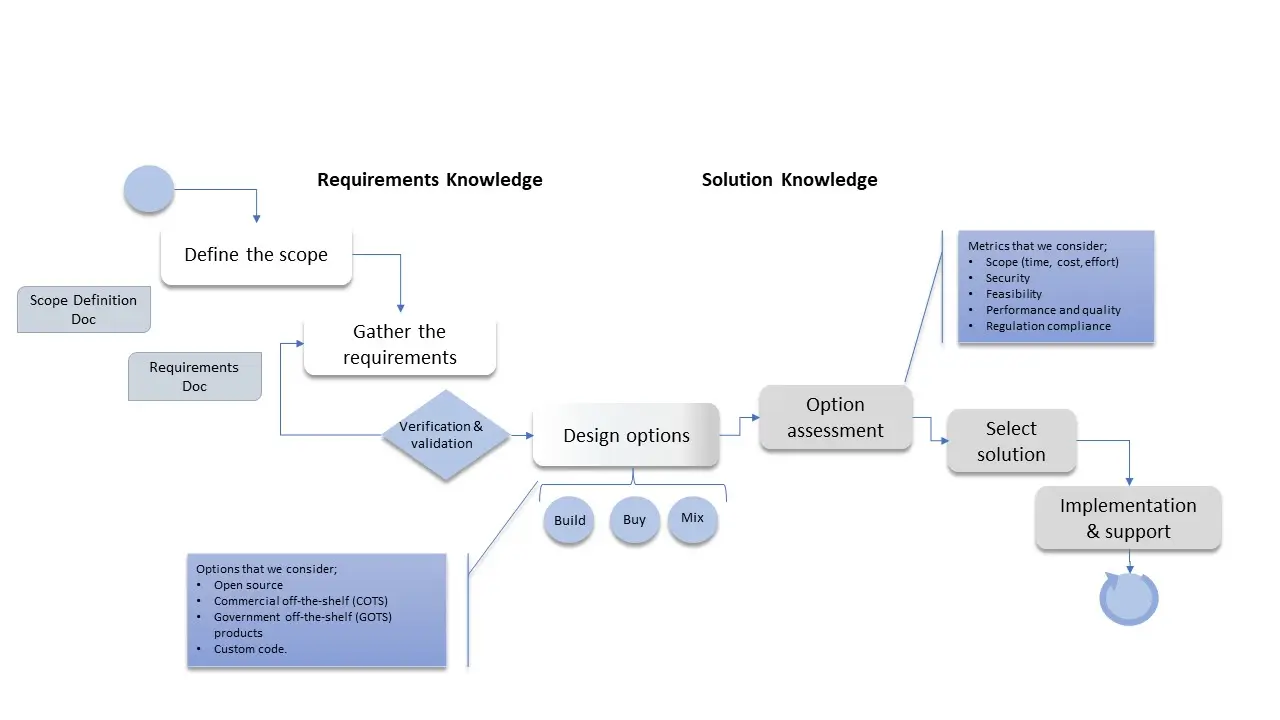
Define the Scope
Stating point for a solution designer, is to understand the customer’s business and define the scope of the project, which includes a visual representation of the problem or opportunity and determining the project’s deliverables and timelines.
Gather the Business Requirements
Once the scope is defined, the solution architecture/solution designer works with the various stakeholders (clients and customers, regulators, technical, developers, test, data) to identify and create the business requirements document with different levels of details, from high level to low level requirements. This includes identifying the functional and non-functional requirements, as well as any constraints or limitations.
Requirement Verification and Validation
The solution architecture team then verifies and validates the technical specifications and requirements to determine that they are accurate and complete. This may include reviewing the functional requirements with stakeholders and subject matter experts, as well as non functional requirements with implementation subject matter experts or technical team.
Solution Design Options or High-Level Design Phase
When it comes to solution design, there are a variety of options available. Some common options include:
Custom code software development This option involves creating a completely new software system from scratch, tailored to the specific needs of the organization. This option has more cost, but it allows for complete flexibility in a functional perspective.
Off-the-shelf software: This option involves purchasing a pre-existing system that is already available on the market. This can be a more cost-effective option, but it may not offer the same level of customization as a custom solution.
Hybrid solution: This option involves a combination of custom system development and off-the-shelf software. This can be a good option for organizations that need some level of customization but also want to take advantage of pre-existing software.
In-house development: This option involves developing a solution within the organization. This can be a good option for organizations that have the resources and expertise to handle the system development in-house.
Outsourcing: This option involves hiring an external company to design and develop the solution. This can be a good option for organizations that want to take advantage of specialized expertise or want to outsource non-core activities.
Ultimately, the best solution design option will depend on the specific needs and resources of the organization. light house solution architecture team evaluates various design options and ideas, and provide you a blueprint of final design.
What Are the Main Solution Categories?
Define each solution as a combination of several elements working together based on business requirements, with general solution categories, for example;
IT Solutions that involve the use of technology to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase revenue. Examples include enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and data analytics platforms and other software solutions .
Business Process Solutions that involve the redesign of business processes to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase revenue. Examples include process automation, Six Sigma and Lean methodologies, and supply chain management.
Cloud Solutions that involve the use of cloud computing to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase revenue. Examples include Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Cyber Security that involve the use of technology to protect against cyber threats, such as hacking, phishing, and malware. Examples include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption.
Digital Transformation that involve the use of digital technologies to transform a business, such as creating a digital customer experience, digital marketing, digital operations, and digital products.
Industry-specific software solution design that are specific to a particular industry, such as healthcare, finance, or retail. Examples include electronic health records systems, online banking software, and point-of-sale systems.
Infrastructure Solutions that involve the design and implementation of the physical infrastructure of an organization such as network, servers, storage, and backup solutions.
Solution Design Option Assessment and Selection
It includes design decisions that involve evaluating different options and selects the most appropriate design option based on factors such as cost, functionality, scalability, and security and other criteria and guidelines. Solution architects are involved in reviewing system design, system specification, technical specification, test, technology and low-level design documents as part of the option assessment and selection process.

Solution Implementation
Documentation assists developers in the technical development. In cases that solutions are provided by other vendors, the solution design team provides services such as project management, implementation, integration, monitoring, maintenance, support, and optimization.
Maintenance and Improvement
Maintenance and improvement is the process of continually updating and enhancing a developed solution to ensure it continues to deliver the expected value for organization and stakeholder.
What Types of Documents Does This Process Create

Navigating the Complexities of Solution Design Documents in a Project
Effective documentation ensure that all stakeholders have a clear understanding of the proposed solution and can make informed decisions throughout the project. Two main categories of solution design documents and detail example is provided.
Technical Documents
In solution design, technical documents are those that describe the technical aspects of the proposed solution, including the hardware, software, and infrastructure required to implement it. Examples of technical documents include:
Network diagrams: diagrams that show the connections and relationships between different network components, such as servers, switches, and routers.
Data flow diagrams: diagrams that show the flow of data through the proposed solution, including the various inputs, processes, and outputs involved.
Process flow diagrams: diagrams that show the flow of work through the proposed solution, including the various tasks, activities, and approvals required.
Hardware specifications: descriptions of the specific hardware components that will be used in the solution, including servers, storage devices, and network equipment.
Software specifications: blueprint of software components that will be used in the solution, including operating software, application software, and middleware.
Security design: Describes the security controls and measures that will be implemented to protect the solution and the data it processes and correspond technology.
Non-Technical Documents
On the other hand, non-technical documents are those that determine the non-technical aspects of the proposed solution, such as project management, processes, and user experience. Examples of non-technical documents include:
- Project charter: A document that outlines the project’s goals, objectives, guidelines, and stakeholders.
- Business process diagrams: diagrams that show the flow of work through the organization, including the various tasks, activities, and approvals required.
- User interface design: Present the solution to the users by creating a detailed description of it, including wireframes and mockups of the user interface.
- Project plan: A document that outlines the project schedule, timelines, and resource allocation in specified cost.
- Acceptance criteria: Assess the project, system or end product by using a list of criteria.
- Risk management plan: Describe the risks associated with the project and developed solution and the mitigation strategies that will be used to address them with a document.





Leave A Comment